Baby development at 3 weeks
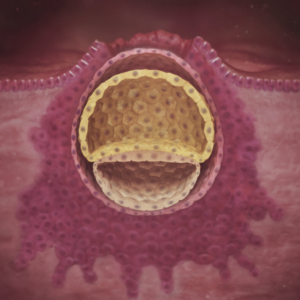
Cells are multiplying
Cells are undergoing rapid multiplication, transforming your developing baby into a small cluster of several hundred cells. These cells are not only multiplying but also embedding themselves into the lining of your uterus. Within this cluster, the cells in the center are destined to form the embryo, while those on the periphery will develop into the placenta – a pancake-shaped organ crucial for supplying your baby with oxygen and nutrients while eliminating waste.
Connecting to you
Establishing a connection with you, your unborn baby is currently relying on a basic circulatory system composed of microscopic tunnels. These tunnels link up with the blood vessels in your uterine wall, facilitating the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste. As the first trimester draws to a close, the placenta will gradually assume this vital role.
3 weeks pregnant body
Early pregnancy hormones
During the early stages of pregnancy, the cells destined to form the placenta actively release the hormone hCG. This hormone signals the ovaries to cease releasing eggs and encourages the ongoing production of progesterone. Progesterone, in turn, prevents the shedding of the uterine lining, safeguarding the developing embryo. A positive pregnancy test result becomes evident when the concentration of hCG in the urine reaches a sufficient level.
Formation of Amniotic Fluid
Within the amniotic sac, the accumulation of amniotic fluid commences. This fluid serves as a protective cushion for the developing baby throughout the ensuing weeks and months. In the event that your water breaks before or during labor, it is this amniotic fluid that may eventually be released.
Pregnancy symptoms during week 3
Lack of Pregnancy Symptoms?
While some women may sense pregnancy even before a positive test, the majority do not. If you’re experiencing symptoms this week, they might resemble premenstrual syndrome (PMS). However, it’s entirely normal if you haven’t felt any changes yet; only half of women experience pregnancy symptoms at 5 weeks pregnant.
Gas and Bloating
The hormone progesterone, which relaxes muscles in your body, including the digestive tract, can lead to gas and bloating. This relaxation slows down digestion, causing discomfort. Constipation affects about half of pregnant women, but staying hydrated and consuming high-fiber foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can help maintain regular bowel movements.
Sore Breasts
Early pregnancy may bring about sore breasts, described by some women as an intensified version of premenstrual discomfort. Swollen, tender, or tingly breasts, along with heightened nipple sensitivity, are common symptoms. As pregnancy progresses, you might observe darkening of the nipples.
Spotting
Light bleeding or spotting may occur this week, known as implantation bleeding. This happens when the fertilized egg implants in the uterus, and it typically lasts one to three days. If you experience bleeding accompanied by pain, contact your healthcare provider immediately, as it could be indicative of an ectopic pregnancy.
Elevated Basal Body
Temperature If you’re tracking your temperature, it should remain high this week. Utilize a basal body thermometer and measure your temperature upon waking up in the morning, before getting out of bed.
Pregnancy checklist at 3 weeks pregnant
Be mindful of your emotions
During the anticipation of whether you’re pregnant or not, experiencing anxiety is normal. If you find yourself stressed or worried, consider discussing your feelings with your partner or a trusted friend. Alternatively, try expressing your concerns by jotting them down in a journal. Engaging in journaling can enhance your emotional well-being, mental clarity, and even physical health.
Avoid excessive heat exposure
While warm baths are generally acceptable during pregnancy, it’s crucial to ensure they are not excessively hot. Steer clear of steam baths, hot tubs, and saunas, as elevated body temperature, particularly in early pregnancy, has been linked to an increased risk of neural tube defects in infants.
Maintain a nutritious diet
Opt for pregnancy-friendly foods such as fruits, vegetables, low-mercury fish, and whole grains. Prioritize foods rich in vitamin C (like strawberries, citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes), iron (found in beef, poultry, soy products, and spinach), and calcium (present in Greek yogurt, fortified cereal, and pasteurized cheese). For snack ideas, explore our list of 10 healthy snacks recommended for expecting moms.
Limit coffee intake
During conception and pregnancy, it’s advisable to restrict caffeine consumption to approximately one cup of coffee per day. Monitoring your caffeine intake is crucial, as excessive amounts can impact both your pregnancy and the well-being of your baby. Familiarize yourself with the caffeine content in various foods and beverages to stay within the recommended daily limit.
Seek support for quitting habits
If you require assistance in quitting smoking, drinking, or substance use, consult your healthcare provider and request a referral to a suitable program or counselor.
Enhance your sleep quality
Prepare for potential sleep disturbances associated with pregnancy in the coming months. Establish healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a consistent bedtime routine and creating a conducive sleep environment in your bedroom.
Ensure safety at work and home
Certain occupations may pose risks to both you and your baby. If you are regularly exposed to chemicals, loud noises, or radiation at work, or if your job involves prolonged standing or heavy lifting, consult your healthcare provider for guidance on maintaining safety during pregnancy. Additionally, be aware of potential hazards in your home, such as lead in drinking water from old pipes, mercury in specific fish, certain pesticides and fertilizers, and cat litter containing feces. Take necessary precautions to protect your developing baby from these potential dangers.
