Baby development at 2 weeks
- Preparing for pregnancy: In recent days, a surge in the hormones estrogen and progesterone has thickened the lining of your uterus to prepare for a potential fertilized egg. Simultaneously, eggs within your ovaries have matured in structures known as follicles.
- The release of an egg: When you ovulate, an egg is released from its follicle and moves from the ovary into a fallopian tube. It’s important to note that ovulation doesn’t always happen exactly in the middle of your menstrual cycle. For instance, in a typical 28-day cycle, ovulation could occur anytime between days 9 and 21.
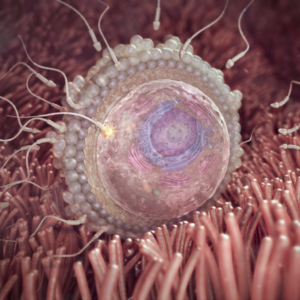
Fertilization
Fertilization Process: Within 24 hours following ovulation, fertilization occurs when a single healthy sperm successfully navigates from the vagina, through the cervix and uterus, into the fallopian tube to penetrate the egg. Though an ejaculation contains nearly 250 million sperm, only about 400 survive the arduous 10-hour journey to reach the egg, and typically just one manages to penetrate its outer membrane.
Genetic Fusion: Over the next 10 to 30 hours, the nucleus of the successful sperm fuses with the nucleus of the egg, combining their genetic material. The sex of the baby is determined at this point: a Y chromosome results in a boy, while an X chromosome results in a girl. The newly formed entity is known as a zygote.
Embryo Development and Implantation: The zygote spends approximately three to four days traveling from the fallopian tube to the uterus, multiplying into 100 or more cells during this journey. Upon reaching the uterus, it becomes known as a blastocyst. Shortly thereafter, it starts embedding itself into the nutrient-rich lining of the uterus, a process known as implantation, setting the stage for further growth and development.
Pregnancy symptoms during week 2
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Changes: A slight increase in basal body temperature is often observed after ovulation.
- Cervical Mucus Changes: The appearance and consistency of cervical mucus can change during ovulation, becoming more slippery and egg-white-like, which facilitates sperm movement.
- Mild Pelvic Pain or Mittelschmerz: Some women may experience mild pelvic discomfort or pain on one side during ovulation.
